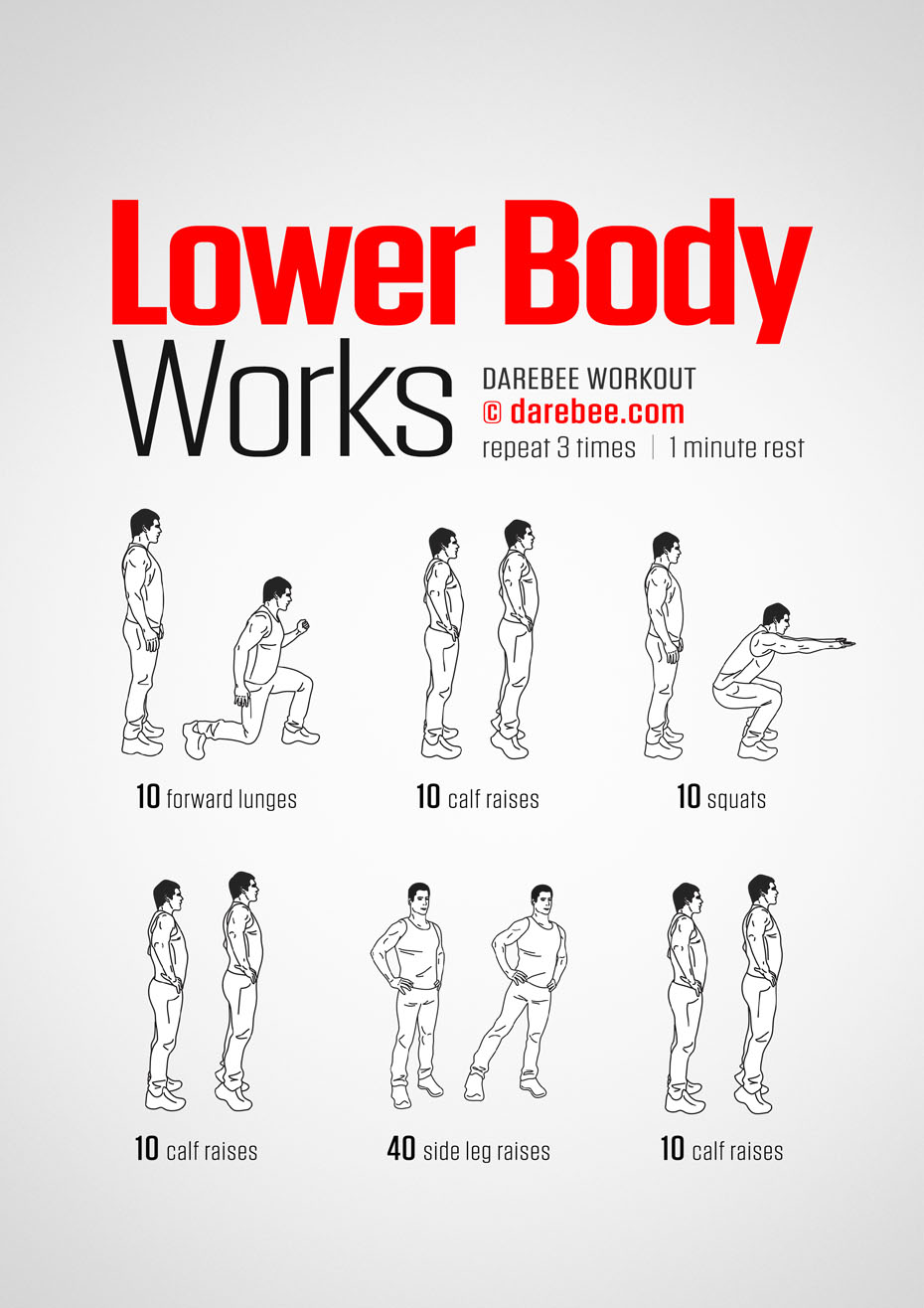
We found that administration of circulating blood factors in plasma from exercised aged mice transferred the effects of exercise on adult neurogenesis and cognition to sedentary aged mice. On the Brain 1.
 The Effects Of Exercise On The Brain Octane Blog
The Effects Of Exercise On The Brain Octane Blog
Exercises to improve balance coordination and agility made a clear impact on the brain structure and cognitive function of a large group of.

Effects of exercise on the brain. Studies have shown that one of the benefits of exercise on the brain is a possible decreased risk of developing diseases like Alzheimers and cancer. It aids the release of hormones which provide an. The Brain and Exercise.
Reversing brain aging may be possible through systemic interventions such as exercise. Exercise affects the brain in many ways. Exercise affects your brain in several ways.
It increases heart rate which pumps more oxygen to the brain. Any form of exercise can help you relax. The Effects of Exercise on the Brain MK McGovern Exercise has been touted to do everything from treat depression to improve memory with the power to cure a host of problems while preventing even more.
The effects of exercise on your mind are so potent that exercise could be considered a psychoactive drug according to a September 2012 study published in the British Journal of Pharmacology. One of the biggest psychological benefits as a result of exercise is that it prevents. Psychological Benefits of Exercise.
The beneficial action of exercise on the brain can be used therapeutically to overcome the effects of consuming a poor diet. What are the Effects of Exercise on the Brain that your clients should know about. The benefits of exercise come directly from its ability to reduce insulin resistance reduce inflammation and stimulate the release of growth factorschemicals in the brain that affect the health of brain cells the growth of new blood vessels in the brain and even the abundance and survival of new brain cells.
Indirectly exercise improves mood and sleep and reduces stress and anxiety. It has been noted that exercise promotes the production of neurotrophins leading to greater brain plasticity and therefore better memory and learning. It has been shown that individuals that develop Parkinsons disease end up losing significant.
In addition to neurotrophins exercise also. The effects of exercise on the brain are profound benefitting health and cognition. Exercise also improves the health and function of existing blood vessels ensuring that brain tissue consistently receives adequate blood supply to meet its needs and preserve its function.
Equally impressive is the action of exercise on cognitive function as documented by studies showing that exercise enhances learning and memory. One of the most significant effects of exercise on the brain is the increased synthesis and expression of BDNF a neuropeptide and hormone in the brain and periphery resulting in increased signaling through its receptor tyrosine kinase tropomyosin receptor kinase B TrkB. For example while experts commonly believed in the past that.
Moving increases your heart rate which brings more oxygen to the brain. It also promotes brain plasticity by stimulating new connections between the cells in numerous important brain areas. Exercise also helps with releasing hormones which provide an excellent environment for brain cell development.
The Effects of Exercise on the Brain The Health Sciences Academy. Studies have shown that physical activity can delay brain ageing. In particular exercise leads to the release of certain neurotransmitters in the brain that alleviate pain both physical and mental.
A quick gym session every other day can increase blood flow to your brain which helps boost brain cell production and thus improve brain health. While the physical benefits of exercise have long been understood exactly which exercises boost brain health is less clear but the more diverse your exercise routine the more likely your brain and cognitive health will benefit along with your body. Exercise-mediated cognitive improvements can be at least partly attributed to neuroplastic changes in the nervous system and may be influenced by the Val66Met polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor BDNF gene.