Fatlipid metabolism is digestion of fat absorption liver synthesized lipoproteins and pile acid recycling. What is fat metabolism.
 Overview Of Lipid Metabolism The Interplay Between The Intestine The Download Scientific Diagram
Overview Of Lipid Metabolism The Interplay Between The Intestine The Download Scientific Diagram
The product of carbohydrate digestion is glucose.
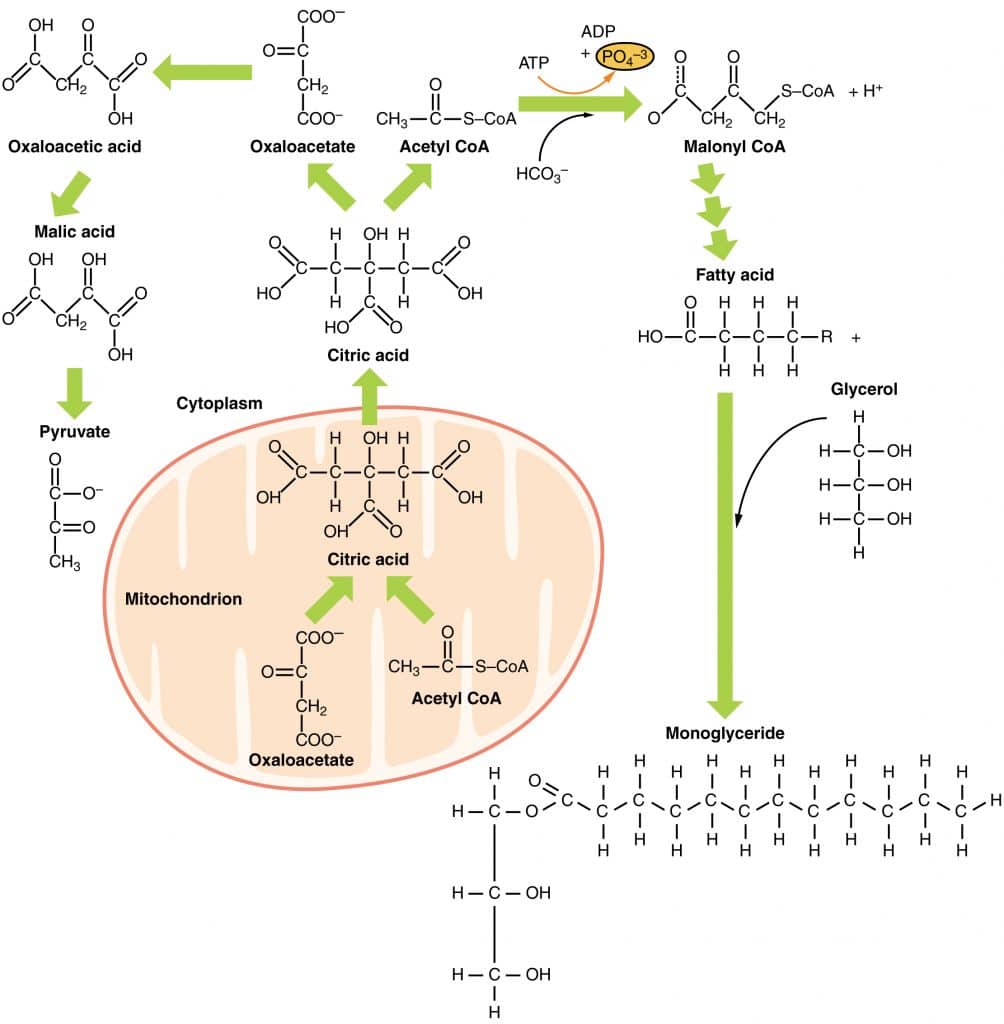
Fat metabolism in liver. Regulation of Fat Metabolism in the Liver. Dysfunction of liver signaling and metabolism can cause metabolic liver disease such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD andor type 2 diabetes. The fate of labelled free fatty acids in isolated perfused livers shows that on entering the liver they are.
By interacting with the intestinal tract and adipose tissue the liver plays a key role in various aspects of lipid metabolism. Liver need s to cope with the incre ased metabol ic dem ands. The liver processes fats to produce other lipids including phospholipids and cholesterol.
The refor e hepatic li pogene sis is c rucial for produc ing better. Ketone bodies provide a metabolic fuel for extrahepatic tissues. Liver energy metabolism is tightly regulated by neuronal and hormonal signals.
A bulk of the lipoproteins are synthesized in the liver. These substances are necessary for cell membrane production digestion bile acid formation and hormone production. Fat Metabolism After digestion fats are also transported to the liver.
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells involving the breakdown or storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids such as those involved in the construction of cell membranes. Nature 215 716 718 1967. THOMAS HK ALFIN-SLATER RB.
14270156 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms. The liver fat accumulating in your liver is not healthy it has metabolic consequences and may raise your blood fat but it can also progress on and affect your liver and make it more inflamed and become very unhealthy. Fat digestion absorption assimilation.
The abnormal states of the body in which an infiltration of the liver for example has been observed include such diverse and unlike cases as diabetes poisoning with phosphorus phlorizin chloroform or alcohol emaciation pernicious diarrhea etc. A considerable number of diseases either border on or are actually classified as attended with an infiltration of fat in some of the organs. Lipid metabolism has a close association with the carbohydrate metabolism.
FAT METABOLISM IN LIVER DISEASE. The liver also metabolizes hemoglobin chemicals medications alcohol and other drugs in the blood. The liver is the ma jor si te of de novo fatty acid synthesi s.
Some cells may die and you could end up with very serious liver disease. Also the liver is tied into the function of the thyroid and its hormones which regulate full body metabolism namely in the conversion of T4 to T3. In this chapter we will summarize fundamental hepatic metabolic processes under normal and diseases conditions.
The liver breaks down many more fatty acids that the hepatocytes need and exports large quantities of acetoacetate into blood where it can be picked up and readily metabolized by other tissues. Fat metabolism in liver diseases authors transl. The liver plays a central role in the detoxification of drugs and poisons as well.
Article in Polish Bojanowicz K Skarbek-Gałamon C Durasiewicz Z Harniewicz M. Arteriosclerosis Carbohydrate Metabolism Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury Cholesterol Dietary Fats Hepatitis Lipid Metabolism Lipidsblood Liver Diseases Proteinsmetabolism Toxicology Substances. Increasing activation of transcription factors such as carbohydrate responsive element binding protein ChREBP sterol response element binding protein-1c SREBP-1c or forkhead box 01 Fox01 may contribute to fatty acid synthesis.
Major examples of the role of the liver in fat metabolism include. Liver Function 4 Fat metabolism - YouTube. A healthy liver with help you burn and discard of excess fata compromised one will slow down that process.
The excess glucose converted into glycogen. The liver is extremely active in oxidizing triglycerides to produce energy. Have a hampered liver and it will also negatively affect your fat burning metabolism.
In animals these fats are obtained from food or. These fats are packaged into protein complexes in the liver and then transported to other cells in the body including the fat-storing cells also known as adipocytes. Fasting also promotes lipolysis in adipose tissue resulting in release of nonesterified fatty acids which are converted into ketone bodies in hepatic mitochondria though β-oxidation and ketogenesis.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/patella-injuries-2548745_FINAL-849bd0d7ed234477939d0398c2b6be4b.png)
/kneepainmedreview-01-5c7d9f26c9e77c0001fd5a7d.png)





